The automotive industry has long been engaged in a quiet but fierce competition over the proportion of hot-formed steel used in vehicle bodies. This material, known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, has become a cornerstone of modern car manufacturing, particularly as safety and efficiency standards grow increasingly stringent. The race to incorporate higher percentages of hot-formed steel isn’t just about marketing—it’s a technological arms race with tangible implications for crashworthiness, fuel economy, and overall structural integrity.
Hot-formed steel, or press-hardened steel, undergoes a unique manufacturing process where it is heated to nearly 900°C before being stamped into shape and rapidly cooled. This treatment transforms the steel’s microstructure, granting it tensile strengths that can exceed 1,500 MPa—far surpassing conventional steels. For automakers, this means the ability to create thinner, lighter components without sacrificing safety, a critical advantage as they balance the demands of electrification, emissions reduction, and consumer expectations.
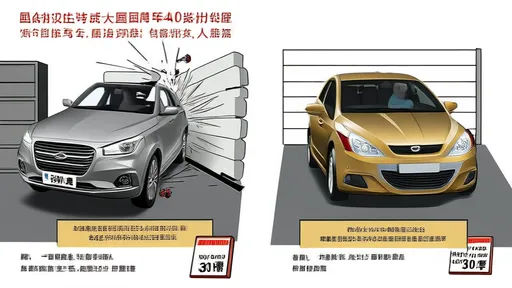
The push for higher proportions of hot-formed steel began in earnest after its successful deployment in luxury and performance vehicles. Early adopters demonstrated that strategic placement of these ultra-strong components—particularly in safety cages, door beams, and crumple zones—could dramatically improve crash test performance. As the technology matured and costs decreased, mainstream manufacturers joined the fray, each seeking to outdo competitors with bold claims about their body structures’ composition.
What makes this competition particularly intriguing is how it reflects broader industry shifts. The transition to electric vehicles has added new urgency to weight reduction efforts, as every kilogram saved translates to extended range. Simultaneously, evolving crash test protocols—especially those addressing small overlap and side-impact scenarios—have forced designers to rethink traditional approaches to structural reinforcement. Hot-formed steel offers solutions to both challenges, making its adoption rates a reliable indicator of a manufacturer’s technical sophistication.
Critics argue that the focus on material percentages can sometimes overshadow more holistic approaches to vehicle safety. A well-designed structure using moderate amounts of high-strength steel might outperform a poorly optimized one with higher proportions. Moreover, the manufacturing complexities of hot-formed steel—its need for specialized presses and precise temperature control—can limit production flexibility and increase costs. These factors have led some automakers to pursue alternative material strategies, blending advanced steels with aluminum or composites.
Despite these considerations, the industry’s trajectory points toward ever-increasing use of hot-formed components. Recent model launches routinely highlight breakthroughs in material science, with some vehicles now featuring over 30% hot-formed steel by weight. The most advanced applications see manufacturers creating tailored blanks—custom-shaped steel pieces with varying thicknesses and properties within a single component—to precisely match strength requirements while minimizing mass.
The competition extends beyond mere percentages into innovative applications. Some manufacturers are experimenting with hot-formed aluminum for certain components, while others focus on optimizing the joining techniques between dissimilar materials. Laser welding, flow drill screws, and advanced adhesives have all seen increased adoption as the industry seeks to maximize the benefits of these high-strength materials without compromising other aspects of vehicle performance.
Looking ahead, the hot-formed steel race shows no signs of slowing. With new steel alloys under development—some promising strengths approaching 2,000 MPa—and continuous improvements in forming technology, the material’s role in vehicle construction seems secure. However, the true winners will likely be those manufacturers who view it not as a standalone solution, but as one element in a comprehensive strategy that includes smart design, advanced manufacturing, and balanced material selection.
For consumers, this technical competition translates to safer, more efficient vehicles—even if most will never know precisely how much hot-formed steel lies beneath their car’s paint. As crash test ratings continue to rise and electric vehicles achieve ever-greater ranges, the quiet battle over material percentages in automotive boardrooms will have proven its worth on roads worldwide.

By /Jun 14, 2025

By /Jun 14, 2025

By /Jun 14, 2025

By /Jun 14, 2025

By /Jun 14, 2025

By /Jun 14, 2025

By /Jun 14, 2025

By /Jun 14, 2025
By /Jun 14, 2025

By /Jun 14, 2025

By /Jun 14, 2025

By /Jun 14, 2025
By /Jun 14, 2025

By /Jun 14, 2025

By /Jun 14, 2025

By /Jun 14, 2025

By /Jun 14, 2025

By /Jun 14, 2025

By /Jun 14, 2025

By /Jun 14, 2025